What is a VFD? What is the operating principle of a VFD?
What is a VFD?
A VFD is a device that converts direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) into adjustable-frequency and adjustable-voltage AC.
Operating principle of a VFD
- The fundamental working principle of a VFD is relatively straightforward. First, single-phase or three-phase AC power is rectified and filtered into a flat DC supply. This process is achieved through a diode rectifier bridge and a capacitor bank. As a result, the power factor (cosphi) of the VFD system remains constant and is independent of the load, typically having a minimum value of 0.96. This DC voltage is then inverted (reversed) into symmetrical three-phase AC voltage. This step is currently accomplished using Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) techniques. Thanks to advancements in microprocessor technology and semiconductor materials, the switching frequency can reach the ultrasonic range, which helps reduce motor noise and minimize losses in the motor’s iron core.
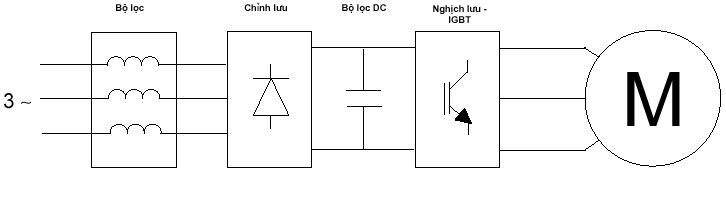
- At the output, a three-phase AC voltage system can smoothly adjust both amplitude and frequency based on the control unit. In theory, there exists a specific relationship between frequency and voltage, depending on the control mode. For loads with constant torque, the voltage-frequency ratio remains constant. However, for pump and fan loads, this relationship becomes a fourth-degree function. Voltage is a fourth-degree function of frequency. Consequently, this leads to torque characteristics that are a second-degree function of speed, tailored to the requirements of pump/fan loads, as torque itself is also a second-degree function of voltage.
- The power conversion efficiency of modern VFD systems is very high, thanks to the utilization of power semiconductor components manufactured using state-of-the-art technology. As a result, energy consumption is approximately equal to the energy demanded by the system.
- Furthermore, contemporary VFDs integrate various control methods suitable for a wide range of different auxiliary loads. Nowadays, VFDs incorporate features such as PID controllers and compatibility with various communication standards, making them well-suited for control and monitoring applications within SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems.
VFD Classification
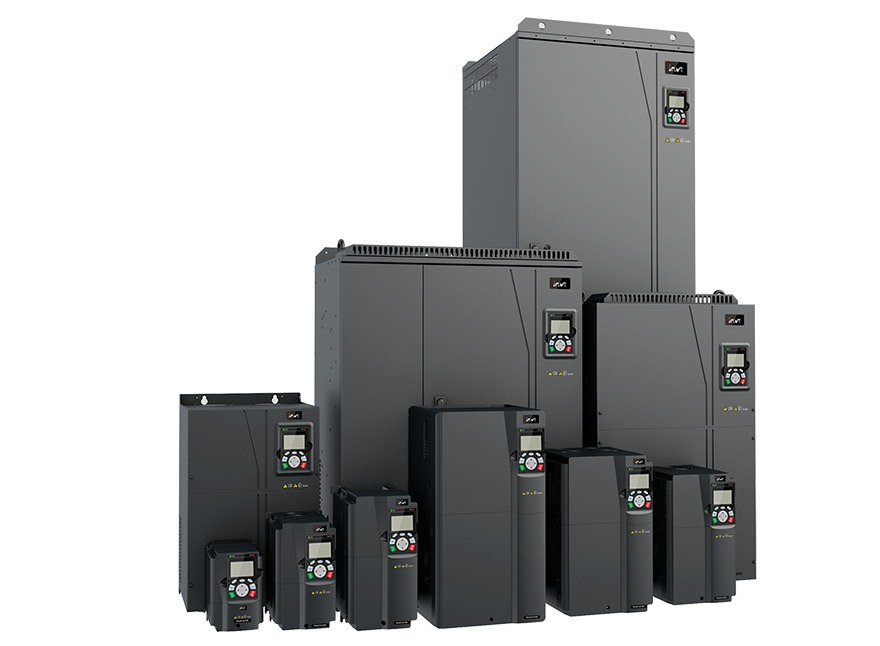
VFDs come in several types, and when classified based on the input power source, there are two fundamental types: Single-phase VFDs and three-phase VFDs. Among these, three-phase VFDs are more widely adopted.
Hướng dẫn lựa chọn các loại biến tần
For selecting the right type of VFD for your application, it’s crucial to clearly identify your application requirements, usage purposes, and balance your investment levels. To make the most suitable inverter choice, consider the following selection principles:
- Match the VFD to Motor Type and Motor Power: Understand the type of motor you intend to drive with the VFD – whether it’s a synchronous or asynchronous motor, single-phase or three-phase, DC or AC, and its voltage requirements. The VFD’s power rating should be equal to or greater than the motor’s power rating.
- Select VFD Based on Application Needs: When choosing a VFD, clearly define your application’s requirements, including desired speed, any advanced control features needed, synchronization requirements, and communication needs. Take into account environmental factors like humidity, high temperatures, dust, or explosion-prone areas. If there are no specific requirements, you can opt for a versatile and commonly used VFD model like GD20 or GD200A. However, for special requirements, choose VFDs with features tailored to your needs.
- Choose VFD Based on Real Load Characteristics: Selecting the right VFD based on your actual load type is essential. Determine whether your machinery has light or heavy loads, operates under short-term or long-term conditions, and whether it operates continuously or intermittently. Select an VFD that suits your specific load characteristics.
- Opt for User-Friendly VFDs for Programming: Consider VFDs that are convenient for programming and offer good support for your application needs. Choose a supplier that provides programming assistance if required.
- Select VFD Matching the Technical Specifications of the Previous Inverter (in case of replacement) or Design Requirements: If you are replacing an existing VFD or have specific design requirements, make sure to select an VFD that matches the technical specifications of the previous unit or meets your design criteria.
- Finally, don’t forget to consider financial factors. For peace of mind, choose an VFD type with a reputable presence and wide availability in the market, robust warranty coverage, stable product quality, durability, and responsive customer service and support, such as those offered by INVT.

Benefits of VFDs
Today, variable frequency drives (VFDs) are no longer a luxury reserved for financially well-endowed enterprises. The benefits they offer far outweigh the costs, making them an indispensable device in every factory. The advantages of using INVT VFDs include:
- Flexible Motor Speed Control to Meet Technological Requirements.
- Effective Energy Savings and Electrical Equipment Protection.
- Motor Protection and Reduced Mechanical Wear.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity.
Important Considerations When Using VFDs
The first step when using VFDs is to carefully read the drive’s specifications provided by the manufacturer, which are specific to each product line. This will help you understand how to properly wire the VFD according to the industry standards. To ensure safety and accuracy, it’s advisable to have reputable companies with highly skilled engineers install and connect the equipment for you. Additionally, you should explore the drive’s supplementary features, such as dust resistance, waterproofing, corrosion resistance, emergency stop buttons, expandability, and more. This knowledge will help you safely and effectively install, operate, and maintain the equipment.
POPULAR VFD BRANDS IN VIETNAM TODAY
1. European-Origin VFDs
- ABB VFDs: Founded in 1988 in Zurich, Switzerland, ABB is one of the popular VFD brands in Vietnam. ABB operates in five areas: electrical equipment, power systems, automation and drives, process automation, and low-voltage electrical equipment.
- Siemens VFDs: Founded in 1847 in Berlin, Germany, Siemens is a global conglomerate in the field of electrical and electronic technology. Siemens operates in over 200 countries, focusing on the fields of electrification, automation, and digitalization.
- SCHNEIDER VFDs: Schneider’s line of VFDs originates from France and has manufacturing facilities in France, China, and Indonesia. It is one of the most popular European-branded VFD lines in the Vietnam market today.
- DANFOSS VFD: Danfoss VFDs come from Denmark and offer excellent water resistance characteristics. They are manufactured both in Denmark and China.
- In addition, there are some less prominent VFD brands like Emerson, Keb, Vacon, Lenze, GE Fanuc, Control Technique, Telemecanique, Allen, and others.
2. Japanese-Origin VFDs
Several Japanese inverter brands, such as Yaskawa, Mitsubishi, Fuji, Panasonic, Hitachi, and Toshiba, are produced in both Japan and China. Japanese VFD brands are known for their higher price points but are trusted for their good quality, stable performance, and some specialized functionalities.
3. Korean-Origin VFDs
LS is a popular Korean-origin VFD brand in Vietnam. These VFDs are relatively more affordable compared to Japanese and European brands.
4. Taiwan-Origin VFDs
Representative Taiwanese VFD brands include Delta and Shihlin. These two inverter lines are quite popular in the Vietname market and are manufactured in Taiwan and China.
5. Chinese-Origin VFDs
Vietnam is a significant consumer market for products originating from China, including VFDs. In the past, Chinese-made VFDs were often associated with lower quality and lower prices. However, with modern technological advancements and investments in research and development, the quality of Chinese-made VFDs has improved significantly. Various Chinese-made VFD brands have entered the Vietnam market, including INVT, Sumo, Inovance, Veichi, Sinee, Gtake, ENC, Powtran, Alpha, Sunfar, Rexrorth, Lion, Hedy, Saj, Chziri, Micno, Chinsc, Senlan, and more. These VFDs come with a range of price points, from average to very affordable. However, choosing a high-quality, reputable, and reasonably priced VFD can be a challenging task for users.
INVT VFDs are highly regarded as high-quality Chinese-made VFDs and are widely used in the Vietnam market with a proven track record of over 14 years. Currently, INVT VFDs are trusted in more than 80 countries and have 9 manufacturing plants, 12 R&D centers, and 850 research and development engineers. In Vietnam, INVT has 3 warranty centers located in Ho Chi Minh City, Hanoi, and Can Tho (under the DAT Corporation) with a warranty period of up to 24 months.
Where to Buy INVT and SIEMENS VFDs?
DAT Group Joint Stock Company is the exclusive distributor of INVT and the exclusive warranty center for INVT in Vietnam. In addition, DAT Group is also the official distributor of SIEMENS in Vietnam. DAT Group specializes in providing products and leading solutions in the Vietnam market in the fields of automation, solar power, energy storage, elevator control, and UPS.
With over 17 years of development, DAT Group has gained the trust and collaboration of more than 10,000 customers nationwide and has been the leading supplier with the highest number of VFDs sold in the Vietnam market for several consecutive years.