What is servo motor?
Servo System
A servo system is a closed-loop control drive system that receives signals and quickly and accurately executes commands from a PLC. The servo system consists of a servo drive, a servo motor, and an encoder for feedback signals from motor to drive. Servos are used for precise position control, adjusting torque for various applications, and achieving extremely fast speed changes (response times in milliseconds).

What is a servo motor? Structure and operating principle of a servo motor?
1. Structure and Classification:
A servo motor is a component within servo system. A servo motor receives signals from controller and provides necessary motion force for machinery when operating at very high speeds and precision.
Servo motors are classified into two types: AC servo motors and DC servo motors. AC servos can handle higher current levels and are typically used in industrial machinery. DC servos are not designed for high currents and are usually suitable for smaller applications.
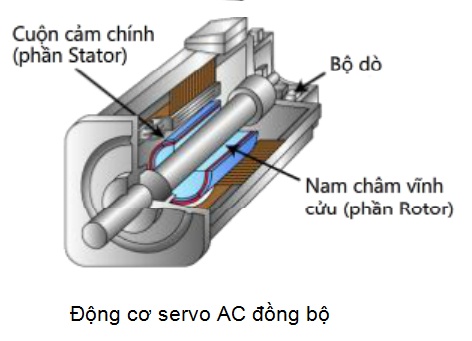
The structure of an AC servo motor includes three main parts: stator, rotor (typically a permanent magnet), and an encoder.
- The stator consists of a coil wound around a core and is powered to provide necessary force to rotate rotor.
- The rotor is constructed with strong permanent magnets.
- The encoder is mounted at the motor’s shaft end to provide accurate feedback on the motor’s speed and position to the controller.
A servo drive is responsible for receiving control signals (pulses/analog) from PLC and transmitting commands to servo motor to control its operation according to given commands. It also continuously receives feedback signals regarding motor’s current position and speed from encoder.

2. Operating Principle:
In principle, a servo motor is an independent device, but it only becomes practical when operating within a servo system.
The servo operation mode is established by closed-loop feedback systems. The servo motor receives a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal from controller to operate and is controlled by an encoder.
When servo motor is in operation, speed and position are fed back to the control circuit through the encoder. If any factors interfere with desired motion and cause speed or position deviations, feedback mechanism sends signals to controller. Based on feedback signals, servo controller compares them to control signals and adjusts accordingly, ensuring that servo motor operates correctly to achieve required speed and precise position.
Benefits of Using AC Servo Systems
- Precise control of speed, position, and torque.
- Fast response times and low inertia (virtually no inertia).
- High operating efficiency (over 90%), minimal heat generation, and minimal vibration.
- High-speed operation and rapid changes in frequency.
- Smooth, lightweight operation, and energy-efficient.
AC servo systems are suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including machine tools, packaging machines, various types of printers, cutting machines, roll-to-roll applications, stop-and-go positioning applications, assembly lines, CNC machines, robotic arms, and more.
With over 17 years of experience in automation and the trust of more than 10,000 customers, DAT is a reliable supplier of genuine products with a large-scale and specialized solution to meet all customer needs and provide the highest efficiency. For more detailed information and consultation, please contact the hotline at 1800 6567 (free of charge).